Connecting to some network resources, promoting products and services on social media, and visiting gaming sites is not always possible due to current restrictions and blocks. The best way to remove such limitations is by using a proxy server. Configuring a virtual IP address allows you to carry out various tasks online without restrictions. Correct proxy selection and setup are important.
Depending on the operating system and browser you use, setting up a proxy may involve different steps for your computer, laptop, or mobile gadget. This article compiles information on preparing both desktop and portable devices running the most common operating systems. The type of software can vary.
Why Use a Proxy? Benefits of Virtual IP Addressing
Almost all internet users have encountered situations where an account is blocked on classified sites, gaming portals, or social networks. Some resources physically located on foreign platforms are inaccessible. These issues are quickly resolved by renting one of the hundreds of available anonymous IPs or a pool of addresses.
Working online with a virtual address is convenient and effective for the following reasons:
- Complete Anonymity: Your computer’s or device’s location and real IP address remain hidden.
- Multiple Accounts: Using a pool of virtual IP addresses lets you connect from many accounts, minimizing the risk of being blocked.
- Access to Restricted Content: A virtual address allows you to download content that may be prohibited from a physical address.
- Data Caching: Most proxies can cache data, reducing traffic usage and speeding up page loads.
- Business & Marketing: Anonymous IPs enable advertising and commercial activities, promoting products and services on social media, classifieds, and supporting data parsing.
- Bypassing Corporate Restrictions: Within a corporate network, configuring an anonymous IP allows you to bypass company-imposed limitations—for example, downloading videos or accessing restricted sites.
Using proxies for personal or professional tasks is the most efficient and accessible approach. It’s quite simple to find a proxy server that meets your needs and budget. After selecting a service, you only need to configure your device or application once to enjoy unrestricted access to network resources.
Features of Configuring Proxies on Windows, Linux, and macOS Devices
If you have a laptop or desktop PC running Windows, you can configure the system on your own. Setting up an anonymous address does not require advanced skills or experience, and it typically takes no more than five minutes. Disabling an anonymous IP is just as easy. You can change your PC’s configuration via the system settings panel without downloading or installing specialized software.
Windows 7: How to Configure the OS for Internet Access via a Virtual IP
All computer settings in this popular OS are adjusted in the system settings submenu. The owner of the device needs to follow several steps:
- Open Control Panel: Click the “Start” menu and go to “Control Panel.”
- Browser Properties: In the search bar, enter the initial characters of the phrase “Browser Properties.” Click the resulting prompt.
- Internet Properties: A new section appears. Go to the “Internet Properties” tab and activate the “Connections” section.
- Network Settings: After you see the “LAN Settings” button, click it and select “Use a proxy server for your LAN.”
- IP and Port: Before configuring, any service you use will give you an IP address and the port through which the connection is made. Enter these details in the relevant fields.
- Exceptions: Depending on your requirements, you can specify websites that should be accessed without the proxy. These fields are generally left blank by default.
Once you save these changes, the new settings are applied. If you need to disable the proxy, repeat the same steps and uncheck the relevant option. Windows 7 configuration can be performed by any user regardless of skill level.
Windows 8: How to Configure the OS for Internet Access via a Virtual IP
If Windows 8 is installed on your computer or laptop, setting up virtual addressing takes just four steps and about five minutes:
- Open Settings: Press “Windows + C” and select “Settings.”
- Network: In the panel that appears, click “Change PC settings,” then choose “Network.”
- Manual Proxy: Select the option to manually set up your proxy server.
- Enter Proxy Details: Fill in the IP address and port provided by your proxy administrator. You can also configure exceptions for visiting certain websites without the proxy.
Be sure to save your settings. They take effect immediately, and no specialized IT assistance is required.
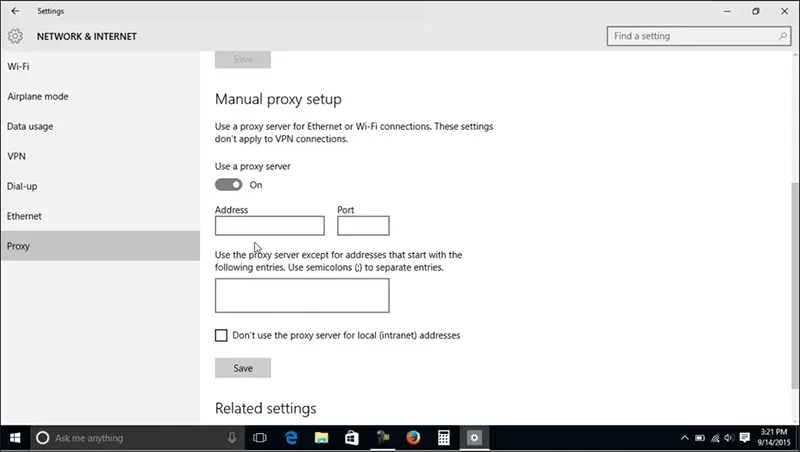
Windows 10: How to Configure the OS for Internet Access via a Virtual IP
Windows 10, the most popular operating system, is also easy to configure for proxy server access. The process should only take about five minutes:
- Search for “Proxy”: In the search bar, type “proxy,” then open “Proxy Settings.”
- Manual Setup: In the new window, choose the “Manual proxy setup” tab and enable manual configuration.
- Enter IP and Port: Fill in the proxy IP address and port given by your administrator.
- Exclusions: If certain sites need to bypass the proxy, list their addresses in the exceptions field.
- Save: It’s crucial to save your settings; otherwise, the anonymous IP won’t be activated.
After configuration, visit any target site that was previously blocked to verify the setup.
Configuring Proxies on MacBooks and Apple Mobile Gadgets
Owners of digital devices often connect to the internet using Apple gadgets. Manually setting these up for anonymous addressing is straightforward and does not require an IT technician’s help, whether you connect via Wi-Fi or 4G.
- System Settings: Go to the settings submenu and select “Network.”
- Advanced Settings: Click “Advanced,” then the “Proxies” tab.
- Select Protocol: Choose your connection protocol, and enter the anonymous IP address and port.
- Authentication: Enter your username and password for proxy access.
- Save: After saving, your device is configured.
It may also be relevant to configure the browser itself—often Safari. The steps are: “Settings” → “Advanced” → “Change Settings” → “Network.” Enter the proxy address and port, then save. Finally, verify that your new settings work properly.
Configuring Proxies on Linux-Based Devices
It can be somewhat more challenging to configure virtual addressing on desktops or mobile devices running Linux. The optimal approach may be to call an IT specialist who knows how to work with this OS. All configuration tasks take place in the command line. If you have the time and inclination to handle it yourself, detailed guidelines are readily available online.
How to Configure Browser Settings for Proxy Use on Different Operating Systems
Browsers are used for personal or business access to internet resources. Some come pre-installed with your OS, while others can be installed separately. Configuring your browser to use a virtual address is not difficult and typically takes only a little time, even for novices.
Configuring Google Chrome
On computers, laptops, and mobile devices, Google Chrome is one of the most commonly used browsers. You can set it up for proxy access by following these steps:
- Open Chrome & Clear History: Launch Chrome and press “Ctrl + H.” In the open tab, select “Clear browsing data” and “Delete data.”
- Search for “Proxy”: In the browser’s search bar, type “proxy.” Then go to the proxy settings submenu.
- System Settings: Once in system settings, click “Use a proxy server.”
- Enter IP and Port: Fill in the IP address and port provided by your proxy administrator. After saving, your requests will go through the selected proxy.
Essentially, configuring the browser redirects you to your OS’s system settings. If needed, you can add exceptions for sites that you’d like to access with your physical IP address.
Configuring Opera
Opera is an alternative to Google Chrome. To configure it:
- Access Settings: Launch Opera and press “Alt + P” to open the settings menu.
- Clear History: Go to “Privacy & Security” to clear your browsing data.
- Search for “Proxy”: Type “proxy” in the settings search bar to open your OS’s system settings.
- Enter Proxy Details: Input the anonymous IP, port, and optional site exclusions.
- Save & Verify: Save your settings and test any previously blocked sites.
The steps are similar regardless of your operating system version.
Configuring Browsers and Specialized Software for Proxy Access
- Internet Explorer: Setup takes about five minutes. After launching it, press “Ctrl + Shift + Del” to clear your browsing history (make sure to leave passwords/forms unchecked). Then go to “Internet Options,” choose “Connections,” and “LAN Settings.” Enter your IP address, port, and any sites to bypass the proxy.
- Firefox: Also requires clearing the cache first. Search for “proxy” in the browser to open manual proxy setup. Enter your proxy parameters and bypass list, then save.
- Yandex Browser: Clear the cache in settings, then head to manual proxy setup. Input the data from your proxy administrator, plus any exceptions you need.
Other browsers on desktop or mobile devices have similar procedures, differing mainly in the key combinations to open their settings menus.
Configuring a Proxy Server on a Router
In many offices and homes, internet access is provided via a router or wireless access point. In such situations, it’s often faster to configure the router itself rather than each device individually. If you have some experience with network equipment, you can handle this on your own:
- Log In: Use the username and password given by your internet service provider to access the router’s admin console.
- Proxy Menu: Locate the submenu for proxy settings and enter the required connection information.
- Save & Reboot: Save the settings and reboot the router. All connected devices will now route their requests through your anonymous IP address. The router uses a WAN interface to connect to the external network.
- Disabling the Proxy: If you no longer need an anonymous IP address, return to the router’s settings, remove or modify the proxy details, and restart the device.
If you encounter difficulties, it’s best to consult an IT specialist.